Getting the Most From Your ERP Functionality
How current ERP functionality and functionality advancements can improve accounting and financial processes.
How current ERP functionality and functionality advancements can improve accounting and financial processes.
Table of Content
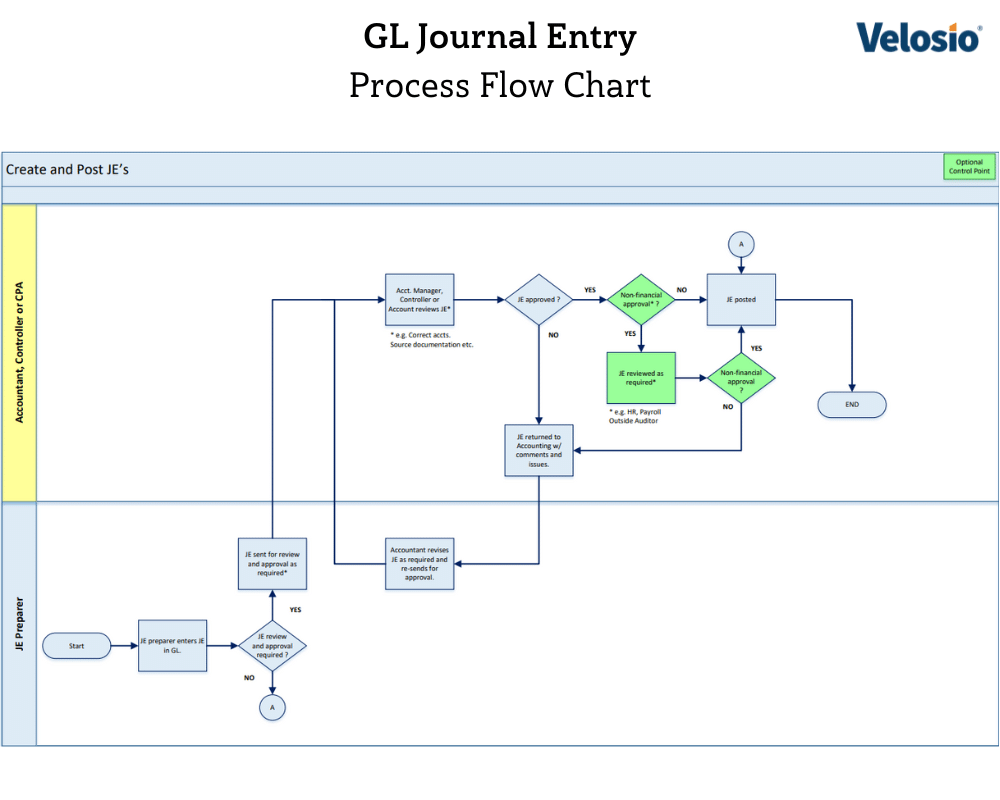
General Ledger, journal entries (JE’s) are made for a variety of reasons. For example, JE’s are used to record GL adjustments, accruals and recurring entries (e.g. depreciation or expense allocations). If external systems are used and not integrated with the GL (e.g. Payroll), JE’s can be used to enter the external system’s transactions into the GL.
JE’s are also used when entering transaction details from other systems using a pre-prepared JE template. JE templates allow the user to build out JE header and line detail (GL accounts, departments etc.) and save the template for future use. This is very useful in streamlining JE entry preparation from high volume external system data. The actual numeric values are entered or copied and pasted into the template. The JE is then saved (i.e. Save As) to allow the original template to remain intact. Some ERPs allow the user build an Excel file in a specific format and use an ERP import tool to process JEs.
JE’s can be static and/or set up to auto-reverse or recur. JEs can be posted to the current period, or to a prior or future period.
Current ERP journal entry functionality is very powerful. Successfully employing the tools available, requires user care and sound, documented processes.
Measures and alerts are meant to assist the user in keeping abreast of processing status, identifying anomalies, and ensuring that implemented process controls are effectively employed. The information below illustrates the interaction between JE functionality and Measures and Alerts.
Functionality- JE Entry and Posting
Measures and Alerts- JE’s prepared and not posted “N” days.
JE’s need to be posted into the GL. Posting should be completed as soon as possible after completion and review/approval. Not posting JE’s in a timely manner, leads to inadvertent omission, which can effect financial reporting accuracy.
Functionality- JE entry and posting, ERP security and system permissions
Measures and Alerts- JE’s prepared and posted by the same user.
An ERP JE is not required to be reviewed and approved prior to posting. This feature can be a potential control weakness. When possible, all JE’s should be reviewed, approved and posted by someone other than the preparer.
Use security settings and permissions to set up a JE review and approval process when needed. Use functionality such as workflow to route the JE’s as required.
This control may create an issue in a small company. At the very least, be sure to have all JE’s reviewed as a part of the monthly or quarterly financial statements review.
Functionality– JE entry and posting, ERP security and process permissions, Flexible JE posting periods
Measures and Alerts- JE’s prepared and posted to an accounting period other than the current period.
The ability to post JE’s to a period other than the current period is supported in most ERPs. Control the process using system roles and permissions. Permissions should be assigned to senior accounting department members, or the outside Accountant.
Posting journal entries to a period other than the current period will have an effect on financial reporting.
For example, a JE posted to a prior period, requires the re-calculation of all financial reports, from the prior period forward to the current period to ensure accuracy.
Functionality– Auto reversing JE’s
Measures and Alerts- Reversing JE’s prepared in the prior period and not reversed in current period.
Reversing JE’s are used primarily for accrual purposes. An accrual is used to record an expense applicable to the accounting period, where the underlying transaction has not yet been processed and posted.
For example, assume that a PO has been prepared for an expense related purchase, the goods or services have been received and/or completed, but the vendor invoice has not yet been vouchered.
The Accounting department reviews all PO’s and vendor invoices meeting this criteria and prepares an accrual entry to record the applicable expense in the proper period. The accrual process is necessary to meet accounting matching standards.
The JE is set as an auto reversing entry (usually reversing in the next accounting period). In some systems, the reversing entry is not automatically posted. If not posted, the expense recorded will “double-up” when the applicable vendor invoice is vouchered and posted.
Functionality– Recurring JE’s
Measures and Alerts- Recurring JE’s not posted.
Recurring entries are used to record transactions which re-occur in more than one accounting period. An example of a recurring entry would be the amortization of a prepaid expense.
Each new recurring entry should be reviewed to ensure posting. In some systems, the subsequent recurring entries are not automatically posted. If not posted, the recurring transaction will not be reflected in the financial statements.
Successfully implementing new ERP functionality isn’t always easy. Consider the best practices below to streamline and control new process implementations.
System permissions and security functionality play an important part in any ERP process. Using these “feature rich” tools, allow the user to set up efficient and controlled processes.
A common JE process permissions example is displayed in the table below:
| Role/Activities | View | New | Edit | Delete |
| Functionality | ||||
| Accountant | ||||
| GL journal entry preparation | X | X | X | NA |
| Recurring and auto-reversing entry preparation | X | X | X | NA |
| Prior and future period entries | X | NA | NA | NA |
| Review and post JE’s | X | NA | NA | NA |
| Accountant (Senior), Controller or CPA | ||||
| GL journal entry preparation | X | X | X | NA |
| Recurring and auto-reversing entry preparation | X | X | X | NA |
| Prior and future period entries | X | X | X | NA |
| Review and post JE’s | X | X | X | NA |
| Measures/ Alerts | ||||
| Accountant | ||||
| JE’s prepared and not posted “N” days | X | NA | NA | NA |
| Accountant, Controller or CPA | ||||
| JE’s prepared and not posted “N” days | X | NA | NA | NA |
| JE’s prepared and posted by the same user | X | NA | NA | NA |
| JE’s prepared and posted to an accounting period other than the current period | X | NA | NA | NA |
| Recurring or auto-reversing JE’s not posted | X | NA | NA | NA |
Talk to us about how Velosio can help you realize business value faster with end-to-end solutions and cloud services.