Supply Chain Analytics: What are They, Why Do They Matter?
Leverage supply chain analytics for efficiency, cost savings, and a competitive edge. Unlock success with data-driven decisions!
Leverage supply chain analytics for efficiency, cost savings, and a competitive edge. Unlock success with data-driven decisions!
Table of Content
Supply chain analytics can help organizations make data-driven decisions, leading to improved customer service, increased profitability, and a competitive edge in the market.
By analyzing historical and real-time data, supply chain analytics can instantly identify patterns, trends, and anomalies. That means, orgs can make proactive decisions that set them up for future success.
In this article, we’ll look at what supply chain analytics entail, why they matter, and how organizations can leverage AI-driven analytics to optimize their supply chain operations.
Supply chain analytics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data from various sources within a supply chain network to gain insights and drive outcomes.
Essentially, it’s about analyzing all data generated by all people, platforms, and processes linked to your SCM practice, then using it to surface insights you can use to improve different aspects of your business. Think – greater operational efficiency, cost savings, happier customers, and so on.
Supply chain analytics involve three main components:
In the Microsoft ebook, Pillars of the Digital Supply Chain, experts explain, in detail, how establishing end-to-end visibility lays the foundation for everything that comes next. It’s literally “pillar number one.”
Once you’ve achieved unity, you can start leveraging analytics tools to understand what’s happening in your supply chain, plan for the future, and take steps toward improving SCM ops.
From there, you can use supply chain analytics with AI, ML, automation, and other next-gen tech to control and optimize key processes – at speed and scale.
Given the ever-increasing complexity of today’s global supply chains, the vital importance of supply chain analytics cannot be overstated.
The idea is that, by leveraging data, organizations gain visibility into their supply chain activities, identify patterns and trends, and make data-informed decisions that optimize processes, mitigate risks, and improve the overall effectiveness of the supply chain.
SC analytics strategies involve the application of analytical methods, statistical techniques, and data mining tools to evaluate and optimize overall supply chain performance.
Types of data:
By combining and analyzing these data sets, organizations can gain insights into their supply chain performance, identify inefficiencies, anticipate disruptions, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions to enhance overall supply chain effectiveness.
Supply chain analytics can also be used to support scenario modeling, simulation, and predictive analytics to forecast future outcomes and evaluate the potential impact of different strategies or decisions on the supply chain.
Basically, SC analytics touch every aspect of the supply chain – and, by extension, the entire org. If you’re still not 100% sold, these next few sections will cover common use cases that put the value of SC analytics in more tangible terms.
In an ebook on building composable supply chains, Microsoft experts warn that “persistent supply chain chaos” can result in data silos, poor visibility, and an inability to leverage advanced technologies like AI, the IoT, and advanced automation.
Composable solutions (like Dynamics 365) allow orgs to design systems from a set of interchangeable modules that connect seamlessly to the various apps and platforms in your network. That way, everyone can access the same information and instantly start using it to inform supply chain decisions.
When all solutions can “talk” to one another and automatically sync data across apps, it enables end-to-end visibility into the supply chain – and everything else.
Real-time visibility across the supply chain is critical for proactively identifying and mitigating risks across all links in the supply chain. But, you need a way to sort all that data before you can use it.
Supply chain analytics tools do exactly that. They minimize risk and build resilience by helping you understand what’s happening within your supply chain, why, and how it all connects to the bigger picture.
For example, you might use predictive analytics and data visualization tools to flag potential disruptions, capture new opportunities, and come up with a game plan (or several) for achieving the right outcomes under various conditions.
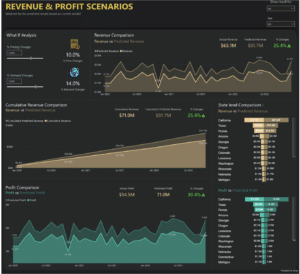
You might use something like this what-if analysis from Power BI community member financedavid12 to prepare for different scenarios – materials shortages, pandemics, workers going on strike, etc.
This visualization measures the predicted impact changes to different variables might have on future revenue and profit outcomes.
Supply chain analytics facilitate continuous improvement by analyzing performance insights against critical KPIs – surfacing issues and inefficiencies so that you immediately start working on fixing them.
Initially, those opportunities tend to be pretty basic – digitizing manual processes or building simple workflows to save employees a little bit of time.
But, analytics tools provide the visibility you need to design processes that feed more real-time insights into said tools – allowing them to develop more accurate and actionable insights over time.
Done right, every process improvement should give you new insights you can use to inform the next round of upgrades.
Say, for example, you want to design a fulfillment optimization journey D365 Intelligent Order Management. The tool allows you to quickly build that process using a rules-based framework and some drag-and-drop edits.
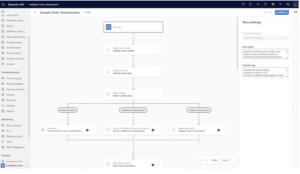
If you’re starting with very little data, you’ll want to make sure you’re capturing the data from that process – and that you’re able to access, interpret, and operationalize it.
From there, you might use D365’s built-in reports, Power BI Insights, etc. to learn more about how that process performs and what you can do to make it better.
Supply chain analytics can also be used to identify needs and solve for them.
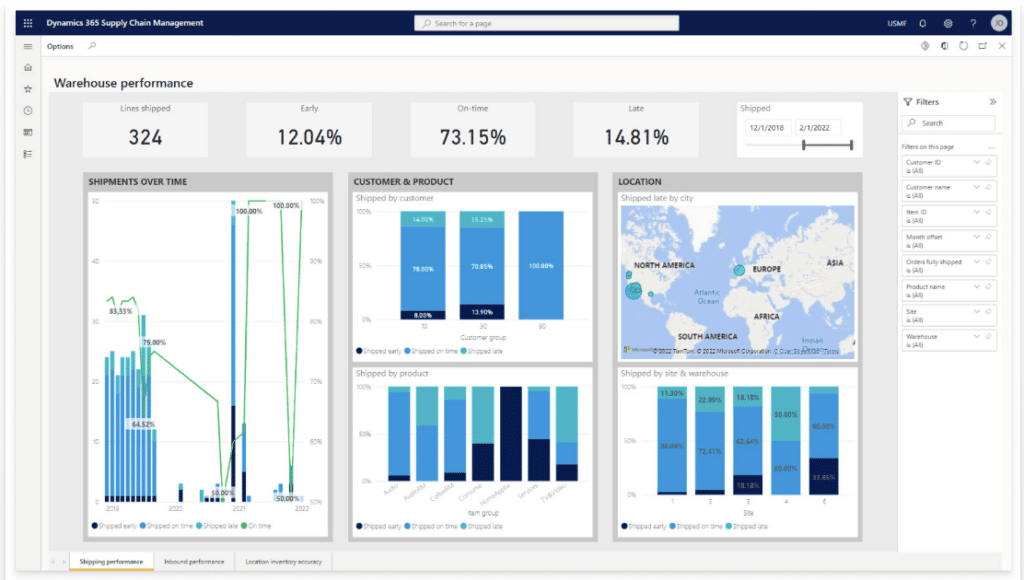
If you look at the dashboard below, you can see a global view of all maintenance requests across all assets with visuals that make it easy to spot patterns that could indicate some sort of problem.
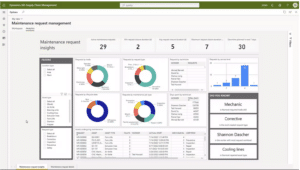
So, maybe you notice that a disproportionate amount of maintenance requests are for inspections.
In that case, you might do some digging to find out what’s causing people to make these requests in the first place, are assets underperforming? Making a weird sound? Causing defects? Once you have an idea of what’s going on, you can start focusing on solutions.
Alternatively, maybe you learn that people keep dropping the ball on preventative maintenance.
If that’s the case, you might then use those asset analytics to build an app that helps workers keep track of service histories, reminds them when service is due, and provides guided workflows to ensure that inspections are performed correctly.
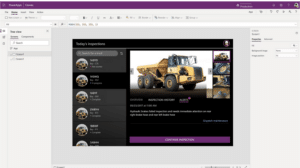
Supply chain analytics also provide valuable insights into supplier performance and procurement strategies.
For example, measuring supplier performance data against KPIs like cost, quality, and on-time deliveries can help you transform your supply chain strategies.
Those insights can help you ID underperforming vendors, strengthen bonds with top-performers, and systematically build a network that aligns with strategic goals.
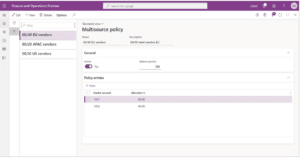
One thing you might do with your supplier data is explore building relationships with a more diverse group of suppliers. Strategies like multisourcing can minimize your reliance on a specific vendor or region and create a more flexible supply chain.
By the way, D365 just added a new multisourcing feature that makes it easier to spread supply across multiple vendors using custom policies.
You might also look for opportunities to build strategic alliances with suppliers. Supply chain orgs are increasingly developing collaborative networks for sharing data, collaborating on products, or splitting logistics costs by bundling shipments together.
In many ways, suppliers are ideal partners. While they might have overlapping interests and audiences, they’re not your competitors – so pooling resources could be an opportunity for growth, innovation, and smoother supply chain ops.
Overall, supply chain analytics enable organizations to optimize their operations, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
By leveraging data and analytics, organizations can make more informed decisions and stay ahead in the dynamic and competitive world of supply chain management.
As technology continues to advance, the future of supply chain analytics holds even more promise, enabling organizations to unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and resilience in their supply chain operations.